Skip to main contentOverview
This document outlines the sequence of operations performed by TypeAuth when processing a request. Understanding this order is crucial for effectively implementing and troubleshooting your authentication and authorization flow.
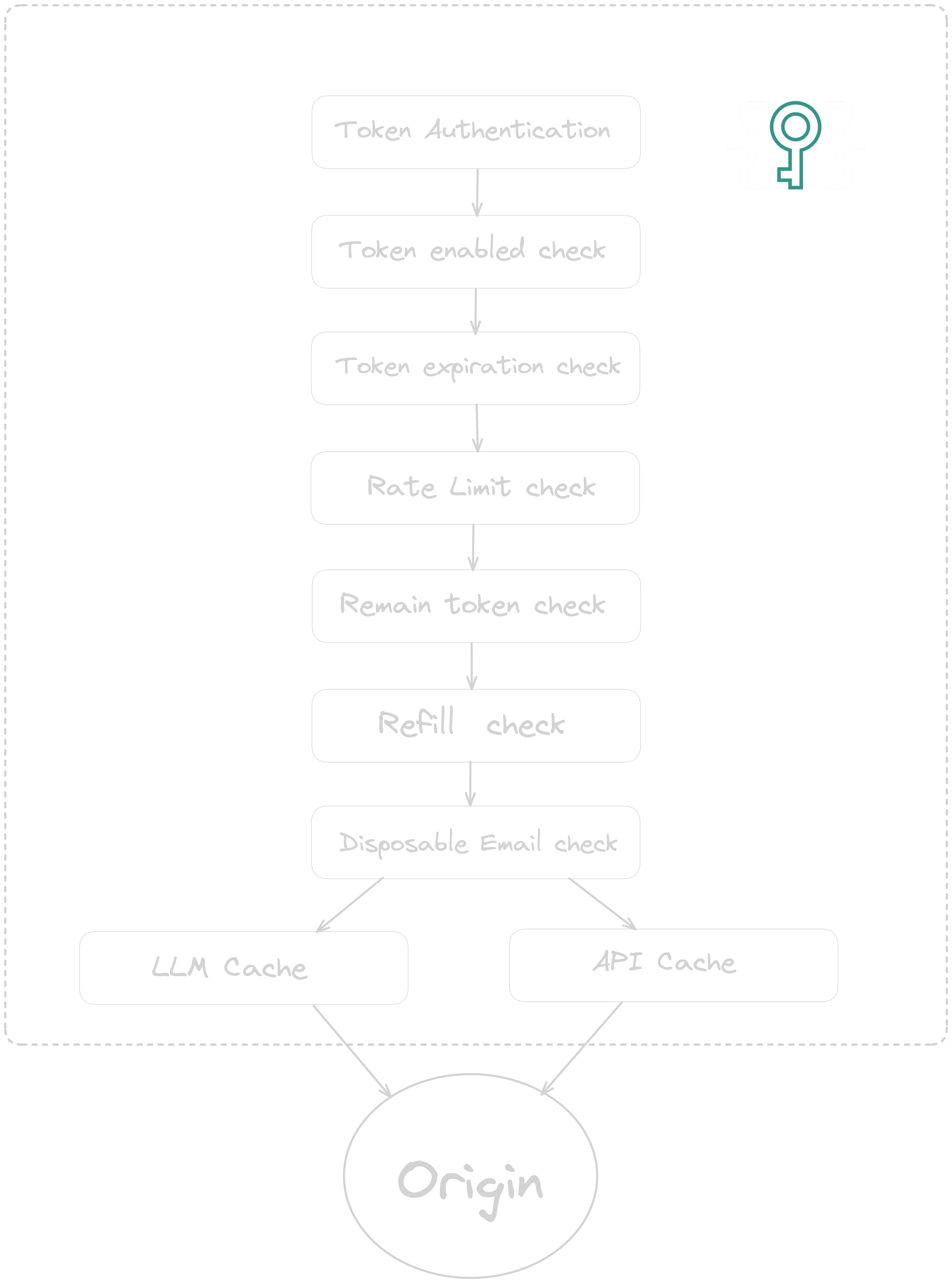
Sequence of Operations
TypeAuth performs the following checks in order:
Authentication
Key Enabled Check
Key Expiration Check
Rate Limit Check
Remaining Requests Check
Key Refill
Disposable Email Check
Cache
Let’s explore each step in detail:
- Authentication
TypeAuth first verifies the authentication of the request. This can be done using either:
- TypeAuth token
- JWT (JSON Web Token)
- Token Enabled Check
Once authenticated, TypeAuth checks if the key associated with the request is enabled.
- Token Expiration Check
If the key is enabled, TypeAuth then verifies whether the key has expired.
- Rate Limit Check
TypeAuth checks if rate limiting is enabled for the application.
- Remaining Requests Check
If rate limiting is enabled, TypeAuth checks if there are any remaining requests allowed within the current time window.
- Key Refill
If necessary, TypeAuth refills the key’s request quota.
- Disposable Email Check
TypeAuth performs a check to determine if the email associated with the request is from a known disposable email service.
- Cache
TypeAuth interacts with the cache, either retrieving or storing information as needed.
- Origin
Finnally if request is not served from Cache will be forwarded to the origin.
Process Flow Diagram
Below is a visual representation of the TypeAuth order of operations: